Discover the power of the Scrum methodology and how it can revolutionize your organization's project management approach.
More...
Embracing the Scrum Methodology for Enhanced Agility and Success
Scrum has become a prominent agile project management framework, enabling organizations from diverse sectors to streamline their processes and achieve remarkable outcomes. This all-encompassing guide delves into the core aspects of this infamous methodology, including its underlying principles, roles, events, and artifacts, equipping you with the knowledge and tools to effectively apply it within your organization.
Key Takeaway
The Scrum methodology emphasizes collaboration, transparency, and value-driven delivery, allowing teams to adapt to changes and continuously improve their processes. By clearly defining roles, utilizing Scrum artifacts, and following Scrum events, organizations can enhance their agility and achieve project management excellence.
Deciphering the Core Principles and Values of Scrum Methodology
The essence of Scrum is rooted in its fundamental principles and values. These cornerstones guarantee transparency, collaboration, and ongoing enhancement for teams employing this agile framework.
Crucial Scrum principles encompass:
Clarifying Scrum Roles: Product Owner, Scrum Master, and Development Team
For the effective execution of the Scrum methodology, it is essential to clearly define and comprehend three primary roles:
Product Owner: Tasked with maximizing the product's value and ensuring the Development Team focuses on high-priority items. They oversee the Product Backlog and collaborate with stakeholders to outline product requirements and objectives.
Scrum Master: A servant-leader who coordinates Scrum events, eliminates obstacles, and coaches the team to adhere to Scrum principles. They collaborate closely with the Product Owner and Development Team to optimize processes and cultivate a high-performing team.
Development Team: A self-organized, cross-functional group accountable for delivering high-quality, potentially releasable increments of the product at the conclusion of each Sprint.
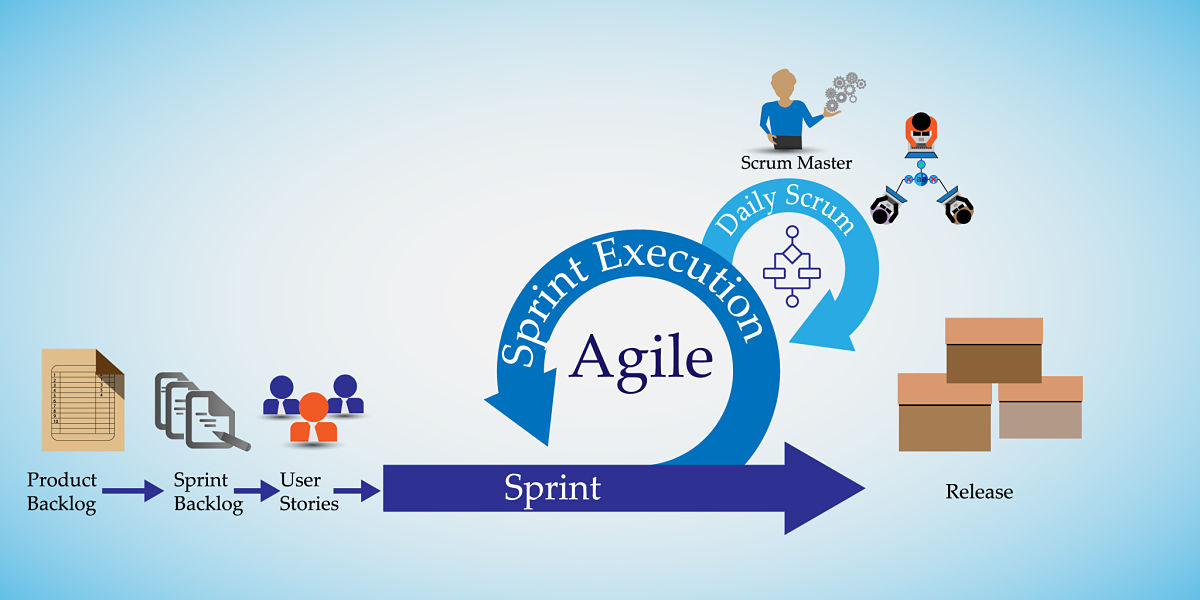
Examining Scrum Artifacts: Product Backlog, Sprint Backlog, and Increment
Scrum artifacts promote transparency and assist teams in monitoring progress throughout the project lifecycle.
Key artifacts consist of:
Fun Fact
The term "Scrum" was initially used in the sport of ruagby to describe a strategy for restarting play, which involved players packing closely together with their heads down to regain control of the ball. This strategy later inspired the Scrum methodology in project management.
Essential Scrum Events:
Scrum events facilitate communication, inspection, and adaptation throughout the project.
Significant Scrum events include:
Sprint: A time-boxed duration, typically spanning two to four weeks, wherein the Development Team works to finalize a potentially releasable Increment.
Sprint Planning: A meeting at the outset of each Sprint where the team strategizes the work to be completed, selecting Product Backlog items for inclusion in the Sprint Backlog.
Daily Scrum: A brief, daily gathering where the Development Team discusses their progress, outlines plans for the day, and identifies any potential roadblocks.
Sprint Review: Conducted at the end of each Sprint, the Sprint Review allows the team to present the work accomplished during the Sprint to stakeholders, gather feedback, and make necessary updates to the Product Backlog.
Sprint Retrospective: A meeting held after the Sprint Review, the Sprint Retrospective enables the team to reflect on their performance, pinpoint areas requiring improvement, and devise an action plan for the subsequent Sprint.
Interesting Fact
The Scrum methodology was first introduced in the early 1990s by Jeff Sutherland and Ken Schwaber, who were software developers looking for a better way to manage complex projects. Today, Scrum is widely used across industries and has been adopted by organizations ranging from small startups to large corporations.
Adopting the Scrum Methodology: A Step-by-Step Approach
To successfully incorporate this methodology within your organization, follow these steps:
- 1Educate and Train: Guarantee that all team members and stakeholders are well-versed in the Scrum methodology, its principles, roles, artifacts, and events
- 2Define Roles: Establish clear guidelines for the Product Owner, Scrum Master, and Development Team roles, ensuring that individuals comprehend their respective responsibilities.
- 3Develop the Product Backlog: Collaborate with stakeholders to generate a prioritized list of desired features, enhancements, and fixes based on customer needs and organizational goals.
- 4Plan the Sprint: Organize Sprint Planning meetings to create a Sprint Backlog, detailing the work to be executed during each Sprint.
- 5Carry Out the Sprint: Have the Development Team work on the Sprint Backlog while adhering to Scrum principles and participating in Daily Scrums to maintain openness and effective communication.
- 6Review and Reflect: At the culmination of each Sprint, conduct a Sprint Review to showcase the Increment and obtain stakeholder feedback, followed by a Sprint Retrospective to identify areas for enhancement and establish an action plan for the upcoming Sprint
- 7Adapt and Iterate: Consistently inspect and adjust the process, incorporating feedback and lessons learned from each Sprint to optimize the Scrum methodology for your organization.
Conclusion
The Scrum methodology is a robust and adaptable agile framework that has revolutionized project management across various industries. By comprehending and implementing its principles, roles, artifacts, and events, organizations can refine their workflows, nurture collaboration, and achieve success in an ever-evolving business environment.
Embrace this methodology to propel your projects and organization towards heightened efficiency, innovation, and value-driven delivery.
In case you are not a Scrum master yet, but you're interested in becoming one, then take a look at the most valuable scrum master interview questions so that you are fully prepared for your new future!
